The Bitcoin deleveraging crisis. As the world’s leading digital asset struggles to regain its footing, investors and analysts are questioning whether Bitcoin can bounce back from this financial deleveraging event. The Bitcoin deleveraging crisis has sent shockwaves through the crypto ecosystem, triggering liquidations, margin calls, and a dramatic reshaping of market dynamics. Within the past few months, Bitcoin’s inability to sustain upward momentum has raised concerns about overleveraged positions, institutional withdrawal, and the broader implications for cryptocurrency adoption. Understanding this crisis is crucial for anyone invested in or considering entering the digital asset space during these challenging times.
What Is the Bitcoin Deleveraging Crisis?
Deleveraging in Cryptocurrency Markets
The Bitcoin deleveraging crisis refers to a widespread unwinding of leveraged positions in the cryptocurrency market, particularly affecting Bitcoin traders and investors. Deleveraging occurs when market participants are forced to reduce their borrowed capital exposure, often resulting from declining asset prices, increased margin requirements, or heightened risk aversion.
In traditional finance, deleveraging typically follows periods of excessive speculation and borrowed capital deployment. The cryptocurrency market, known for its high leverage offerings—sometimes up to 100x or more—is particularly vulnerable to rapid deleveraging events. When Bitcoin’s price drops significantly, traders using leverage face margin calls, forcing them to either add more collateral or close their positions, which further accelerates downward pressure.
The Trigger Points of the Current Crisis
Several factors contributed to the current Bitcoin deleveraging crisis:
Market Overextension: Before the crisis, Bitcoin had experienced substantial leverage buildup, with open interest in futures and perpetual contracts reaching all-time highs. This created an unsustainable market structure prone to violent corrections.
Regulatory Pressure: Increased scrutiny from global regulators, particularly regarding cryptocurrency exchanges and their leverage offerings, has prompted many platforms to reduce maximum leverage ratios and tighten risk management protocols.
Macroeconomic Headwinds: Rising interest rates, inflation concerns, and traditional market volatility have driven investors away from risk assets, including Bitcoin. The correlation between Bitcoin and tech stocks has meant that broader market selloffs impact cryptocurrency prices.
Institutional Repositioning: Large institutional players who entered the market during the previous bull run have been reassessing their crypto allocations, with some reducing positions or implementing more conservative risk management strategies.
How the Bitcoin Deleveraging Crisis Impacts Market Recovery
Liquidation Cascades and Price Suppression
One of the most visible effects of the Bitcoin deleveraging crisis has been the series of liquidation cascades that have prevented sustainable price recovery. When Bitcoin attempts to rally, overleveraged long positions accumulate, creating conditions for sharp reversals. Conversely, when prices decline, these positions are forcibly closed, creating selling pressure that pushes prices lower.
Data from major cryptocurrency exchanges shows that billions of dollars in leveraged positions have been liquidated during recent months. These liquidation events create a self-reinforcing cycle: falling prices trigger more liquidations, which cause further price declines, triggering even more forced selling.
Reduced Market Liquidity and Volatility Spikes
The Bitcoin deleveraging crisis has significantly impacted market liquidity. As traders reduce their leverage and position sizes, the order books on exchanges have thinned, making it easier for large orders to move the market substantially. This reduced liquidity creates an environment where volatility increases, making it more difficult for Bitcoin to establish stable price levels necessary for sustained recovery.
Market makers, who typically provide liquidity by maintaining buy and sell orders, have also become more cautious during the deleveraging period. Wider bid-ask spreads and reduced depth mean that even modest trading volumes can result in significant price movements, creating an uncertain environment for both short-term traders and long-term investors.
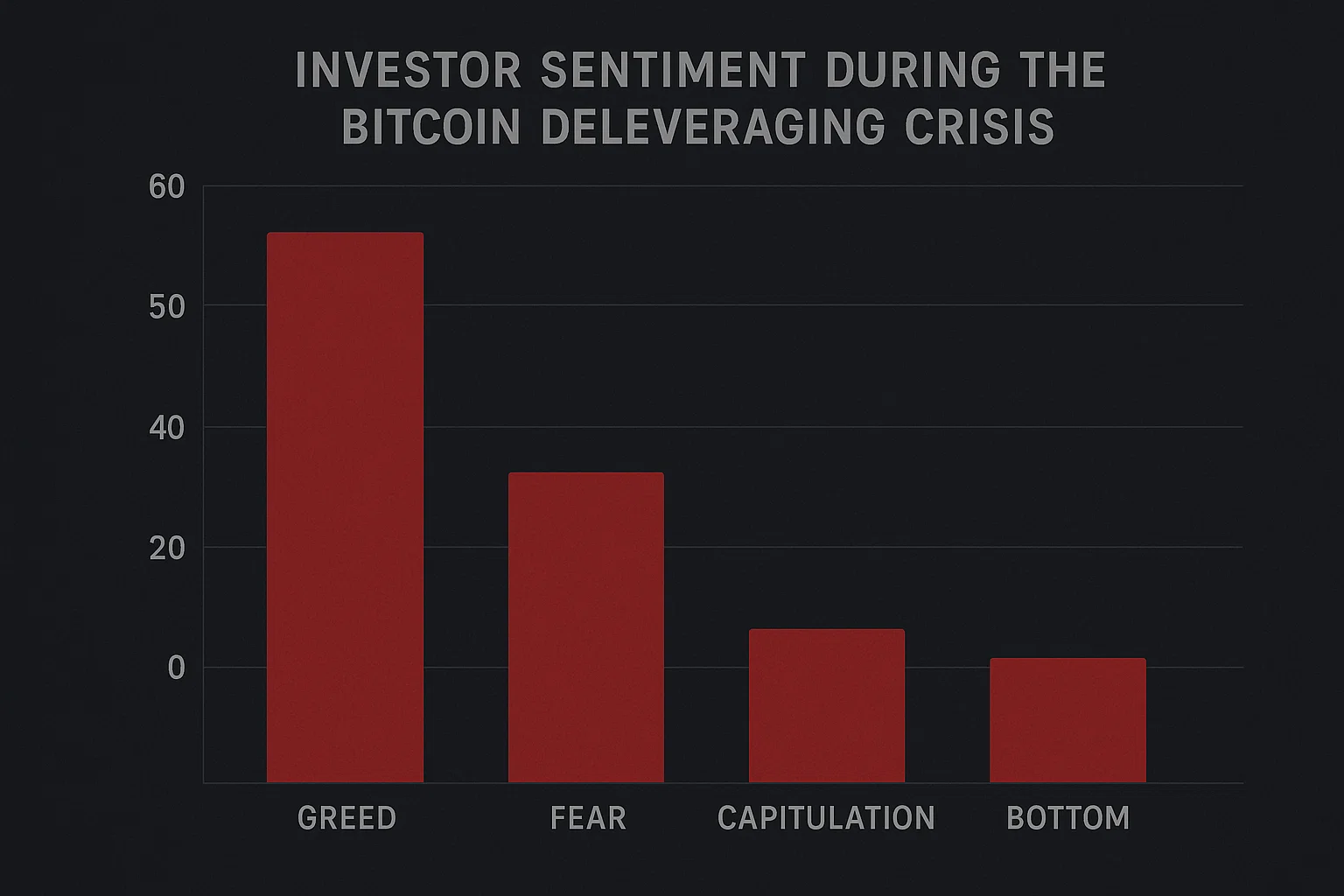
Investor Sentiment During the Bitcoin Deleveraging Crisis
Fear and Uncertainty Dominate the Market
Investor psychology plays a crucial role in the Bitcoin deleveraging crisis and subsequent recovery attempts. The Fear and Greed Index, a popular sentiment indicator for cryptocurrency markets, has remained in “fear” or “extreme fear” territory for extended periods during the crisis. This negative sentiment creates a self-fulfilling prophecy where investors are reluctant to enter the market, limiting the buying pressure needed for recovery.
Social media sentiment analysis and Google Trends data reveal declining interest in Bitcoin during the deleveraging period. Search volume for terms like “buy Bitcoin” has decreased substantially, while queries related to “Bitcoin crash” and “sell Bitcoin” have spiked during price declines. This shift in search behaviour reflects broader uncertainty about Bitcoin’s near-term prospects.
Institutional Investors Adopt Wait-and-See Approach
Institutional participants, who were once heralded as the driving force behind Bitcoin’s mainstream adoption, have adopted a more cautious stance during the Bitcoin deleveraging crisis. Many hedge funds and asset managers are waiting for a clearer market structure and reduced volatility before committing additional capital to Bitcoin positions.
However, it’s important to note that not all institutional interests have disappeared. Several major financial institutions continue developing Bitcoin-related products and services, suggesting that long-term conviction remains intact despite short-term market challenges. The difference lies in risk management—institutions are now more selective about entry points and position sizing compared to the exuberance of previous market cycles.
Technical Analysis: Bitcoin’s Struggle for Support
Key Support and Resistance Levels
From a technical perspective, the Bitcoin deleveraging crisis has erased several critical support levels that previously acted as price floors. Bitcoin has struggled to maintain positions above psychologically significant levels, repeatedly testing and sometimes breaking through support zones that held firm during previous corrections.
Technical analysts point to several key resistance levels that Bitcoin must overcome to signal a genuine recovery from the deleveraging crisis. The 200-week moving average, historically a reliable indicator of Bitcoin’s long-term trend, has served as both support and resistance during this period. A decisive break above this level would represent a significant technical achievement and potentially attract momentum-based buyers back to the market.
Trading Volume Patterns and Market Structure
Volume analysis reveals important insights about the Bitcoin deleveraging crisis. During price declines, trading volume has been elevated, indicating genuine selling pressure rather than a simple lack of buyer interest. However, during recovery attempts, volume has often been insufficient to sustain upward momentum, suggesting that many market participants remain on the sidelines.
The futures market structure has also provided clues about market sentiment during the crisis. The relationship between spot prices and futures prices (the basis) has fluctuated significantly, sometimes indicating hedging activity or bearish positioning through contango markets. Funding rates on perpetual contracts, which reflect the cost of holding leveraged positions, have periodically swung from positive to negative, showing shifts between bullish and bearish sentiment.
Comparing the Current Crisis to Historical Deleveraging Events
The 2018 Bear Market Parallels
The current Bitcoin deleveraging crisis shares several characteristics with the 2018 bear market that followed Bitcoin’s surge to nearly $20,000 in late 2017. Both periods featured excessive leverage buildup during euphoric market conditions, followed by sharp corrections that forced widespread position closures.
However, important differences exist between the two events. The current crisis occurs in a more mature market with greater institutional participation, more sophisticated trading infrastructure, and considerably more regulatory oversight. Additionally, Bitcoin’s adoption as a treasury reserve asset by several companies and the launch of spot Bitcoin ETFs in various jurisdictions represent structural changes that didn’t exist during the 2018 downturn.
Lessons from the March 2020 COVID Crash
The March 2020 market crash, when Bitcoin dropped nearly 50% in a single day, provides another relevant comparison point for understanding the Bitcoin deleveraging crisis. That event featured similar liquidation cascades and forced deleveraging, but recovery was swift, fueled by unprecedented monetary stimulus and a flight to alternative assets amid traditional market uncertainty.
The current crisis lacks the same catalysts for rapid recovery. Central banks have shifted from expansionary to contractionary monetary policy, removing a key driver of risk asset appreciation. This fundamental difference suggests that recovery from the current deleveraging event may follow a different trajectory—potentially slower but more sustainable—than the V-shaped recovery seen in 2020.
Regulatory Impact on the Bitcoin Deleveraging Crisis
Global Regulatory Crackdowns on Leverage
Regulatory developments have significantly contributed to the Bitcoin deleveraging crisis. Authorities in multiple jurisdictions have implemented or proposed restrictions on the leverage available to retail traders. The European Union’s Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) regulation, the United States’ increased enforcement actions, and various Asian countries’ crypto restrictions have all played roles in reshaping the market landscape.
These regulatory pressures have forced many cryptocurrency exchanges to reduce maximum leverage offerings, implement stricter Know Your Customer (KYC) requirements, and enhance risk disclosures. While these measures aim to protect investors from excessive losses, they’ve also contributed to the deleveraging process by making it more difficult and expensive to maintain highly leveraged positions.
Impact on Exchange Operations and Market Access
The regulatory environment has also affected how exchanges operate during the Bitcoin deleveraging crisis. Some platforms have exited certain jurisdictions entirely rather than comply with new regulations, reducing market access for traders in those regions. Others have delisted certain trading products or implemented deposit limits that constrain traders ‘ability to add margin to positions facing liquidation.
These operational changes have fragmented the global Bitcoin market to some degree, potentially affecting price discovery and creating arbitrage opportunities between different regulatory regimes. The reduced availability of high-leverage products has also shifted some trading activity to offshore or unregulated platforms, raising concerns about investor protection and market integrity.
The Role of Bitcoin Miners in the Deleveraging Crisis
Miner Capitulation and Selling Pressure
Bitcoin miners have faced their own challenges during the Bitcoin deleveraging crisis, contributing to market pressures. Declining Bitcoin prices combined with rising energy costs have compressed mining profitability, forcing some operations to sell their Bitcoin holdings to cover operational expenses.
This miner capitulation—when miners are forced to sell Bitcoin at a loss—has historically coincided with market bottoms, as it represents capitulation by one of the most committed participant groups in the ecosystem. However, during the current crisis, the situation is complicated by the fact that many mining operations had taken on debt during the previous bull market, adding financial obligations that require regular Bitcoin sales regardless of price levels.
Hash Rate Fluctuations and Network Security
The Bitcoin deleveraging crisis has also manifested in Bitcoin’s hash rate—the computational power securing the network. As unprofitable miners shut down equipment, the hash rate has experienced periods of decline, although Bitcoin’s difficulty adjustment mechanism has helped maintain network stability.
Interestingly, despite short-term fluctuations, Bitcoin’s hash rate has shown remarkable resilience overall, suggesting that the most efficient mining operations continue operating and that new capacity is still being deployed. This resilience provides some reassurance about Bitcoin’s fundamental strength even as price struggles continue.
Potential Catalysts for Bitcoin Recovery
Macroeconomic Shifts and Fed Policy
Recovery from the Bitcoin deleveraging crisis may ultimately depend on broader macroeconomic conditions. A shift in Federal Reserve policy toward lower interest rates or renewed quantitative easing could reignite interest in risk assets, including Bitcoin. Historically, Bitcoin has performed well in environments of monetary expansion and currency debasement concerns.
Some analysts argue that the current deleveraging represents a necessary market cleansing that will create a more sustainable foundation for future growth. By removing excessive leverage and speculative excess, the market may be positioning itself for a fundamentally driven bull market based on actual adoption and utility rather than leverage-fueled speculation.
Institutional Adoption and ETF Developments
Despite the Bitcoin deleveraging crisis, developments in institutional infrastructure continue. The approval and launch of spot Bitcoin ETFs in various markets represents a significant milestone in Bitcoin’s maturation. These products provide regulated access to Bitcoin exposure without the complexities of self-custody, potentially attracting a new wave of institutional and retail capital.
Major financial institutions continue building Bitcoin-related services, from custody solutions to trading desks and lending products. This ongoing infrastructure development suggests that institutional conviction in Bitcoin’s long-term prospects remains intact, even if short-term positioning has become more cautious.
Technological Improvements and Network Upgrades
Bitcoin’s technological development continues regardless of market conditions, with improvements to scaling solutions like the Lightning Network and Taproot adoption potentially enhancing Bitcoin’s utility and value proposition. As these technologies mature, they could provide fundamental support for Bitcoin’s value independent of speculation-driven price movements.
The growth of Bitcoin-based financial products, including wrapped Bitcoin on other blockchain platforms and Bitcoin-backed lending and borrowing protocols, expands Bitcoin’s utility beyond simple speculation. These developments create additional use cases that could support demand even in a deleveraged market environment.
Investment Strategies During the Bitcoin Deleveraging Crisis
Dollar-Cost Averaging and Long-Term Accumulation
For investors navigating the Bitcoin deleveraging crisis, strategic approaches to accumulation have taken precedence over leveraged speculation. Dollar-cost averaging—systematically purchasing fixed dollar amounts regardless of price—has gained popularity as a way to build positions during market uncertainty without attempting to time the exact bottom.
This approach aligns with the investment philosophy of many long-term Bitcoin believers who view current prices as attractive relative to Bitcoin’s potential over multi-year timeframes. By avoiding leverage and focusing on spot purchases with capital they can afford to allocate for extended periods, these investors position themselves to benefit from eventual recovery without facing liquidation risk.
Risk Management and Position Sizing
The Bitcoin deleveraging crisis has reinforced the importance of proper risk management for cryptocurrency investors. Position sizing—determining how much of a portfolio to allocate to Bitcoin—has become more conservative, with many financial advisors recommending smaller allocations than during the height of previous bull markets.
Diversification within cryptocurrency portfolios has also evolved, with some investors maintaining exposure to alternative cryptocurrencies or Bitcoin-adjacent investments like mining companies, blockchain infrastructure stocks, or crypto-related financial services. This diversification approach aims to capture upside from cryptocurrency adoption while managing downside risk from continued Bitcoin price volatility.
Future Outlook: Will Bitcoin Overcome the Deleveraging Crisis?
Bull Case Scenarios
Optimistic analysts believe Bitcoin will emerge stronger from the Bitcoin deleveraging crisis, arguing that the current market reset creates opportunities for sustainable growth. The bull case rests on several pillars: Bitcoin’s fixed supply schedule creating scarcity value, growing institutional infrastructure supporting easier access, increasing global economic uncertainty driving alternative asset interest, and continued technological improvements enhancing utility.
Additionally, the halving event scheduled for 2024—which reduced new Bitcoin supply by 50%—typically creates supply-side pressures that have historically preceded significant price appreciation. If the deleveraging process concludes before or shortly after the halving, the combination of a cleaned-up market structure and reduced supply could create favourable conditions for recovery.
The bear case also suggests that Bitcoin may have reached a level of market maturity where exponential growth rates are no longer achievable, meaning recovery might be more modest than previous bull cycles. If Bitcoin transitions from a high-growth speculative asset to a more stable store-of-value, the character of its price movements and investor expectations may need to adjust accordingly.
Conclusion
The Bitcoin deleveraging crisis represents one of the most significant challenges facing the cryptocurrency market in recent years. Understanding the complex dynamics driving this crisis—from overleveraged positions and regulatory pressures to macroeconomic headwinds and miner capitulation—is essential for anyone involved in the digital asset ecosystem.
While Bitcoin struggles to bounce back from this deleveraging event, the long-term fundamentals supporting Bitcoin’s value proposition remain largely intact. The current crisis may ultimately serve as a necessary market correction that removes excessive speculation and creates a more sustainable foundation for future growth.
Read More: Bitcoin to $75K or $125K: Price Prediction Analysis