The financial services industry stands at a pivotal crossroads where traditional banking systems meet revolutionary technology. An innovative blockchain framework for banking is transforming how financial institutions secure transactions, manage data, and serve customers. As cyber threats escalate and customers demand faster, more transparent services, banks worldwide are exploring blockchain technology as a cornerstone of their digital transformation strategies. This comprehensive guide explores how blockchain frameworks are strengthening security protocols while simultaneously boosting operational efficiency across the banking sector.
Within the first quarter of 2024, over 67% of major financial institutions reported active blockchain initiatives, signaling a massive shift toward decentralized ledger technology. The blockchain framework for banking represents more than just a technological upgrade—it’s a fundamental reimagining of how financial transactions are recorded, verified, and protected. From reducing fraud to accelerating cross-border payments, blockchain technology addresses critical pain points that have plagued the banking industry for decades.
Blockchain Framework for Banking Operations
A blockchain framework for banking consists of a distributed ledger system that records transactions across multiple nodes, creating an immutable and transparent record of all financial activities. Unlike traditional centralized databases, where a single entity controls all data, blockchain technology distributes information across a network of computers, making unauthorized alterations virtually impossible.
Core Components of Banking Blockchain Architecture
The architecture of a robust blockchain in financial services includes several fundamental components that work synergistically to deliver enhanced security and performance:
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) forms the foundation, maintaining synchronized copies of transaction records across all network participants. This redundancy ensures that even if one node fails or becomes compromised, the integrity of the entire system remains intact.
Consensus Mechanisms validate transactions without requiring a central authority. Whether using Proof of Work, Proof of Stake, or Byzantine Fault Tolerance algorithms, these mechanisms ensure all participants agree on the validity of transactions before they’re permanently recorded.
Smart Contracts automate complex banking processes, executing predetermined conditions without human intervention. These self-executing contracts reduce processing times from days to minutes while eliminating manual errors and intermediary costs.
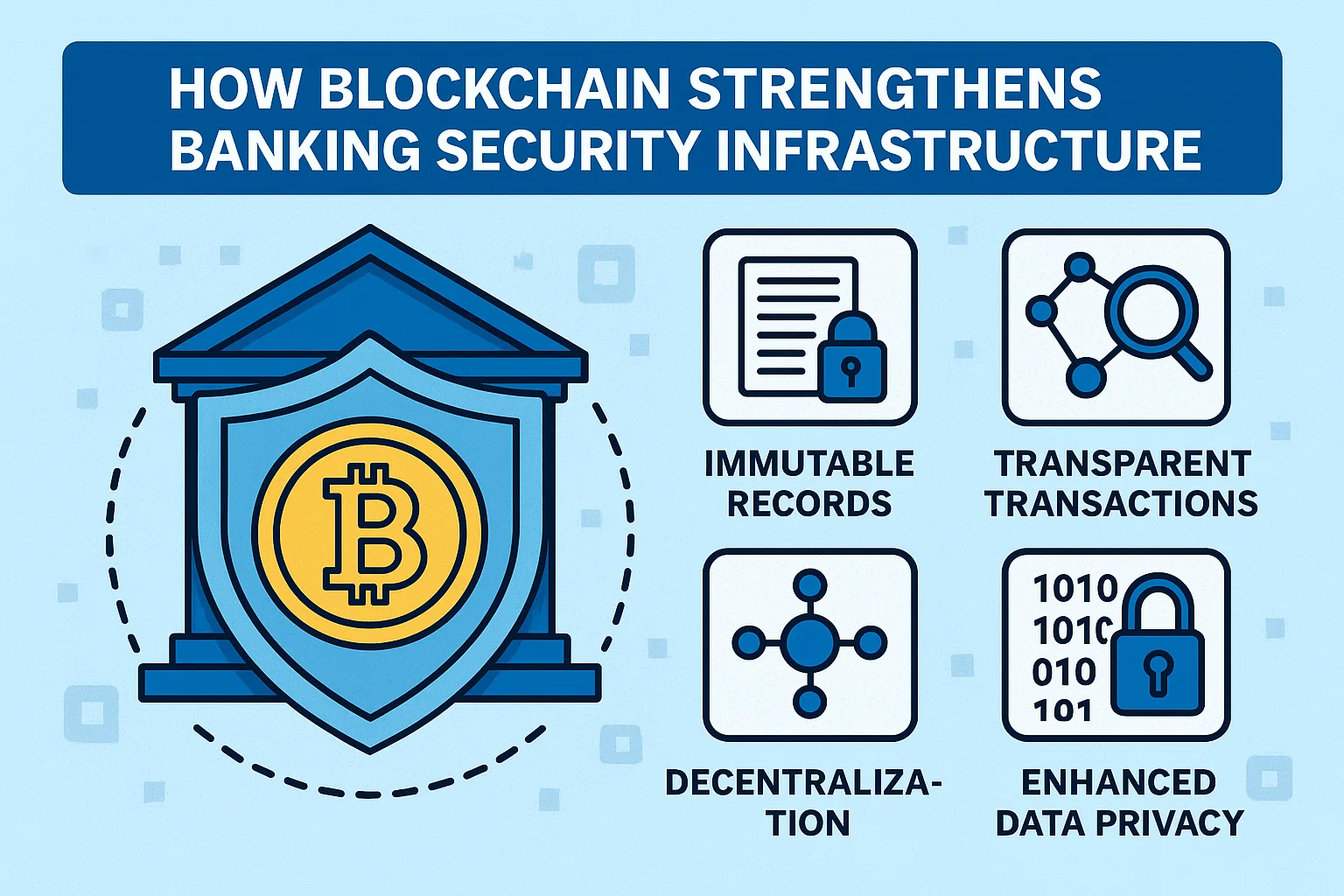
Cryptographic Security protects data through advanced encryption techniques, ensuring that only authorized parties can access sensitive financial information. Each transaction is secured with unique cryptographic signatures that are mathematically impossible to forge.
Types of Blockchain Networks in Banking
Financial institutions implement different blockchain configurations based on their specific requirements:
Permissioned Blockchains restrict network participation to verified entities, making them ideal for interbank transactions where regulatory compliance and privacy are paramount. These networks offer the security benefits of blockchain while maintaining the control banks need for regulatory reporting.
Hybrid Blockchain Solutions combine public and private elements, allowing banks to keep sensitive customer data private while sharing transaction verification with a broader network. This approach balances transparency with confidentiality.
Consortium Blockchains enable multiple banking institutions to collaborate on a shared infrastructure, reducing costs while maintaining competitive advantages. These networks are particularly effective for payment processing and trade finance applications.
How Blockchain Strengthens Banking Security Infrastructure
Security remains the primary driver behind blockchain adoption in financial services. The blockchain framework for banking security addresses vulnerabilities that traditional systems cannot effectively mitigate.
Eliminating Single Points of Failure
Traditional banking systems concentrate data in centralized servers, creating attractive targets for cybercriminals. A single successful breach can compromise millions of customer records. Blockchain technology in banking distributes data across numerous nodes, eliminating these single points of failure. Even if hackers compromise individual nodes, they cannot alter the blockchain without controlling a majority of the network—a practically impossible feat in well-designed systems.
Immutable Transaction Records
Once recorded on a blockchain, transactions cannot be altered or deleted. This immutability creates an audit trail that regulators, auditors, and compliance officers can trust implicitly. Every modification attempt is visible to all network participants, making fraud detection instantaneous rather than reactive.
Financial institutions have reported up toan 80% reduction in fraud-related losses after implementing blockchain-based verification systems. The technology’s transparency ensures that suspicious patterns are identified and flagged in real-time, preventing fraudulent transactions before they are completed.
Enhanced Identity Verification and KYC Compliance
Blockchain solutions for banks revolutionize Know Your Customer (KYC) processes through decentralized identity management. Instead of each bank maintaining separate identity verification systems, blockchain enables a shared, secure identity platform where customer information is verified once and trusted across multiple institutions.
This approach reduces the estimated $500 million banks collectively spend annually on redundant KYC procedures while improving customer experience. Customers complete verification once, and their authenticated identity credentials are securely shared across participating banks with their explicit consent.
Real-Time Fraud Detection Through Smart Contracts
Smart contracts embedded within the blockchain framework for banking continuously monitor transactions for anomalous patterns. These automated systems can flag suspicious activities—such as unusual transfer amounts, geographic inconsistencies, or rapid sequential transactions—within milliseconds, allowing banks to freeze potentially fraudulent transactions before completion.
Machine learning algorithms integrated with blockchain frameworks learn from historical fraud patterns, continuously improving detection accuracy. This proactive approach contrasts sharply with traditional reactive fraud detection systems that often identify problems only after significant losses occur.
Boosting Operational Efficiency Through Blockchain Implementation
Beyond security enhancements, blockchain technology transforms banking efficiency across multiple operational dimensions.
Accelerating Cross-Border Payment Processing
International payments traditionally require 3-5 business days and pass through multiple intermediary banks, each adding fees and delays. Blockchain banking solutions reduce this timeline to minutes or even seconds by eliminating intermediaries and enabling direct peer-to-peer transfers.
Ripple’s blockchain network, for example, processes international payments in under four seconds at a fraction of traditional costs. Banks using blockchain for cross-border transactions report a 40-70% reduction in processing costs while improving transaction speed by over 90%.
Streamlining Trade Finance Operations
Trade finance involves complex documentation processes with letters of credit, bills of lading, and numerous compliance documents passing between exporters, importers, banks, and customs authorities. Paper-based processes create bottlenecks, with transaction cycles often extending to weeks or months.
A blockchain framework for trade finance digitizes these documents as verifiable digital assets, enabling instantaneous sharing and verification. All parties access the same immutable record, eliminating discrepancies and disputes. Banks implementing blockchain in trade finance report a 50% reduction in processing times and a 30% decrease in operational costs.
Automating Regulatory Compliance and Reporting
Financial institutions face increasingly complex regulatory requirements, spending billions annually on compliance activities. Blockchain-based compliance systems automatically generate audit trails and regulatory reports by recording every transaction with complete transparency.
Regulators can access real-time transaction data (with appropriate permissions), enabling continuous monitoring rather than periodic audits. This shift from reactive to proactive compliance reduces regulatory costs while improving oversight quality.
Reducing Settlement Times for Securities Trading
Securities settlement typically requires T+2 (trade date plus two days) to complete, creating counterparty risk and tying up capital. Blockchain settlement systems enable near-instantaneous settlement, reducing this timeline to minutes. The Australian Securities Exchange’s blockchain-based CHESS replacement system promises same-day settlement, releasing billions in trapped capital and reducing systemic risk.
Real-World Applications and Use Cases
Leading financial institutions worldwide have moved beyond pilot programs to production-scale blockchain implementations in banking.
JPMorgan’s Onyx Platform
JPMorgan’s Onyx blockchain platform processes over $1 billion in daily transactions, focusing on wholesale payment systems and repurchase agreements. The platform demonstrates that enterprise blockchain for banks can operate at the scale required for major financial institutions.
HSBC’s FX Everywhere Platform
HSBC’s blockchain-based foreign exchange settlement platform has processed over $6 trillion in transactions since launch. The system provides real-time transparency into FX trades while reducing settlement risk and operational costs.
Santander’s Blockchain-Based International Payments
Santander’s One Pay FX service uses Ripple’s blockchain technology to offer same-day or next-day international transfers to retail customers. The service operates across multiple countries, demonstrating that blockchain banking solutions can scale to consumer-facing applications.
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
Multiple central banks are developing or piloting blockchain-based digital currencies. China’s digital yuan, the Bahamas’ Sand Dollar, and Sweden’s e-krona represent government-backed blockchain frameworks for national banking systems. These initiatives could fundamentally transform monetary policy implementation and payment systems.
Overcoming Implementation Challenges
Despite its promise, implementing a blockchain framework for banking presents significant challenges that institutions must address strategically.
Regulatory Uncertainty and Compliance Concerns
Cryptocurrency-related regulatory ambiguity creates hesitation among financial institutions. Banks must ensure their blockchain implementations comply with evolving regulations across multiple jurisdictions. Engaging proactively with regulators, participating in industry consortia, and designing flexible frameworks that can adapt to regulatory changes helps mitigate these concerns.
Integration with Legacy Banking Systems
Most banks operate decades-old core banking systems that weren’t designed for blockchain integration. Creating middleware solutions that bridge legacy systems and blockchain platforms requires substantial investment and technical expertise. Gradual migration strategies—implementing blockchain for specific use cases while maintaining existing systems—provide practical paths forward.
Scalability and Performance Requirements
Public blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum face throughput limitations that are unacceptable for banking operations processing thousands of transactions per second. Permissioned blockchain networks designed specifically for financial services can achieve transaction speeds comparable to traditional systems while retaining blockchain’s security benefits.
Layer-2 scaling solutions, sharding, and hybrid architectures further enhance blockchain performance, making them viable for high-volume banking operations.
Interoperability Between Different Blockchain Networks
As banks adopt various blockchain platforms for different purposes, ensuring these systems can communicate becomes critical. Industry standards like ISO 20022 and initiatives like the Interwork Alliance work toward blockchain interoperability, enabling seamless data exchange between different networks.
Skills Gap and Talent Acquisition
Blockchain development requires specialized skills that are scarce in the current talent market. Banks must invest in training existing IT staff, partnering with blockchain technology providers, and competing for limited blockchain expertise. Building internal blockchain competency centers helps institutions develop sustainable blockchain capabilities.
Future Trends in Blockchain Banking Technology
The evolution of blockchain frameworks for financial institutions continues to accelerate, with several emerging trends shaping the future landscape.
Integration with Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Combining blockchain and AI in banking creates powerful synergies. AI algorithms analyze blockchain data to detect fraud patterns, predict market trends, and personalize customer experiences, while blockchain provides the secure, transparent data foundation AI systems need.
Quantum-Resistant Cryptography
As quantum computing advances threaten current cryptographic standards, banks are developing quantum-resistant blockchain protocols. These next-generation systems will secure financial data against future quantum attacks, ensuring long-term security.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Integration
While currently operating primarily in cryptocurrency markets, DeFi protocols offer innovative financial services without traditional intermediaries. Banks are exploring how to integrate DeFi concepts—such as automated market makers and yield farming—into regulated banking frameworks, potentially transforming lending, investing, and asset management.
Tokenization of Traditional Assets
Blockchain asset tokenization converts real-world assets—including real estate, commodities, and securities—into digital tokens that can be traded on blockchain platforms. This innovation promises to increase liquidity, reduce transaction costs, and democratize access to investment opportunities previously available only to institutional investors.
Enhanced Privacy Technologies
Zero-knowledge proofs and other privacy-preserving technologies enable blockchain transactions to be verified without revealing underlying details. These innovations address privacy concerns while maintaining blockchain’s transparency benefits, making the technology more acceptable for sensitive banking operations.
Implementing a Successful Blockchain Strategy
Financial institutions considering blockchain adoption in banking should follow strategic implementation frameworks to maximize success probability.
Conducting a Comprehensive Feasibility Assessment
Before committing resources, banks must evaluate which processes would benefit most from blockchain implementation. Use cases with multiple parties, frequent reconciliation needs, or significant fraud risk typically offer the highest return on investment.
Starting with Pilot Programs
Rather than attempting enterprise-wide blockchain transformation, successful banks begin with limited pilot programs targeting specific pain points. These pilots demonstrate value, identify challenges, and build organizational knowledge before scaling.
Building Strategic Partnerships
Collaboration with technology providers, other financial institutions, and industry consortia accelerates blockchain implementation while sharing development costs. Organizations like R3’s Corda consortium and the Enterprise Ethereum Alliance provide frameworks for collaborative blockchain development.
Prioritizing User Experience
The most sophisticated blockchain banking solution fails if customers find it difficult to use. Designing intuitive interfaces that abstract away blockchain complexity ensures customer adoption and satisfaction.
Establishing Governance Frameworks
Clear governance structures defining decision-making processes, access controls, and dispute resolution mechanisms are essential for multi-party blockchain networks. Well-designed governance prevents conflicts and ensures network sustainability.
Measuring ROI and Success Metrics
Evaluating blockchain implementation success requires defining clear metrics aligned with organizational objectives.
Quantitative Performance Indicators
- Transaction Processing Speed: Measuring reduction in settlement times
- Cost Savings: Calculating decreased operational expenses
- Fraud Reduction: Tracking declines in fraud-related losses
- Customer Acquisition: Monitoring growth in customer base attracted by blockchain-enabled services
Qualitative Success Factors
- Customer Satisfaction: Assessing improvements in user experience
- Regulatory Compliance: Evaluating enhanced compliance capabilities
- Innovation Reputation: Measuring brand perception as a technological leader
- Employee Engagement: Tracking staff enthusiasm for blockchain initiatives
Conclusion
The blockchain framework for banking represents a transformative force reshaping financial services fundamentals. From fortifying security infrastructure against increasingly sophisticated cyber threats to streamlining operations and reducing costs, blockchain technology delivers tangible benefits that justify the investment and effort required for implementation.
Financial institutions that strategically adopt blockchain solutions for banks position themselves competitively for the digital economy. Those hesitating risk falling behind more agile competitors and failing to meet evolving customer expectations for faster, more transparent, and more secure banking services.
Read More: Blockchain IoT Industrial Revolution The Future Is Here